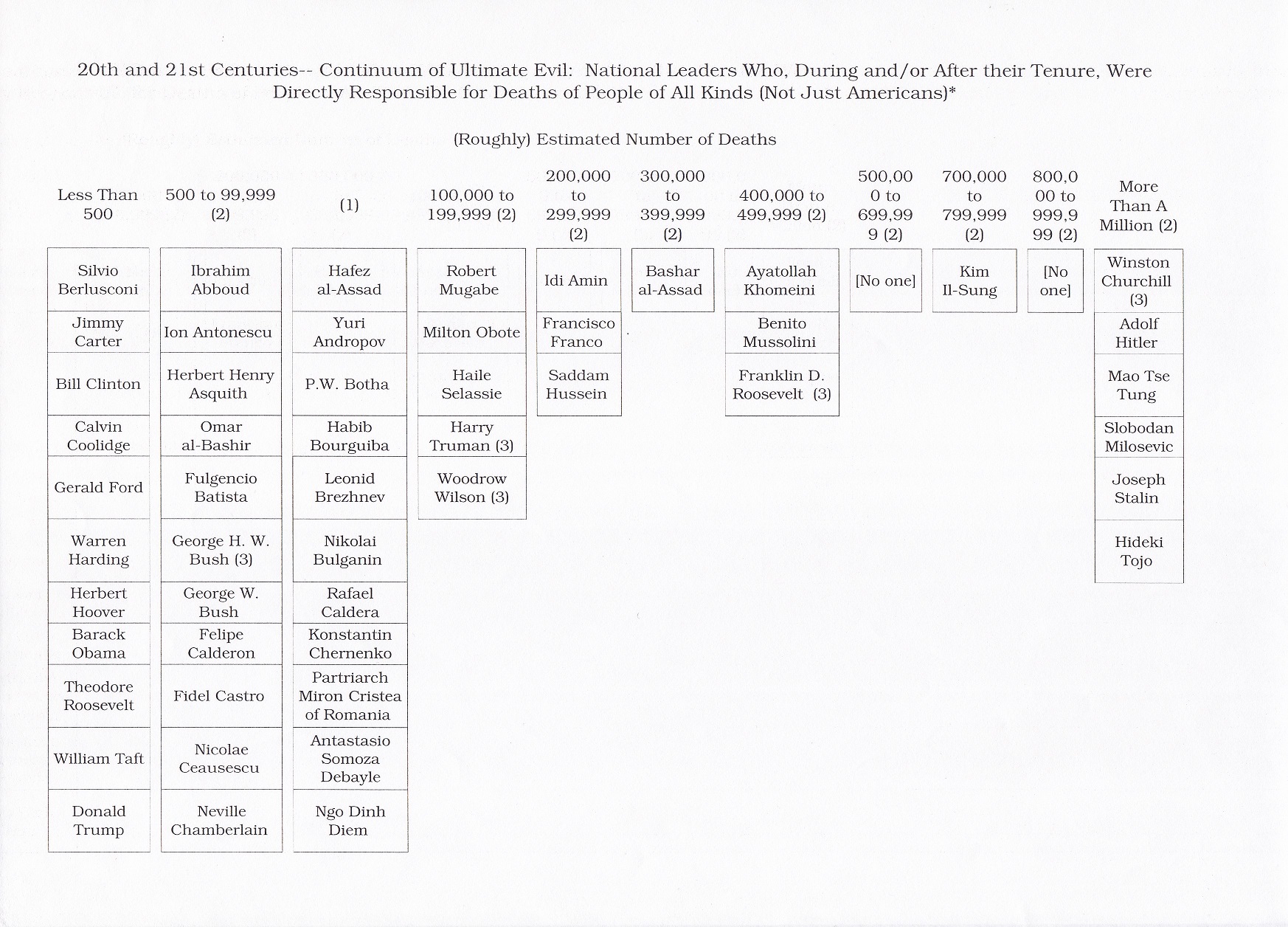
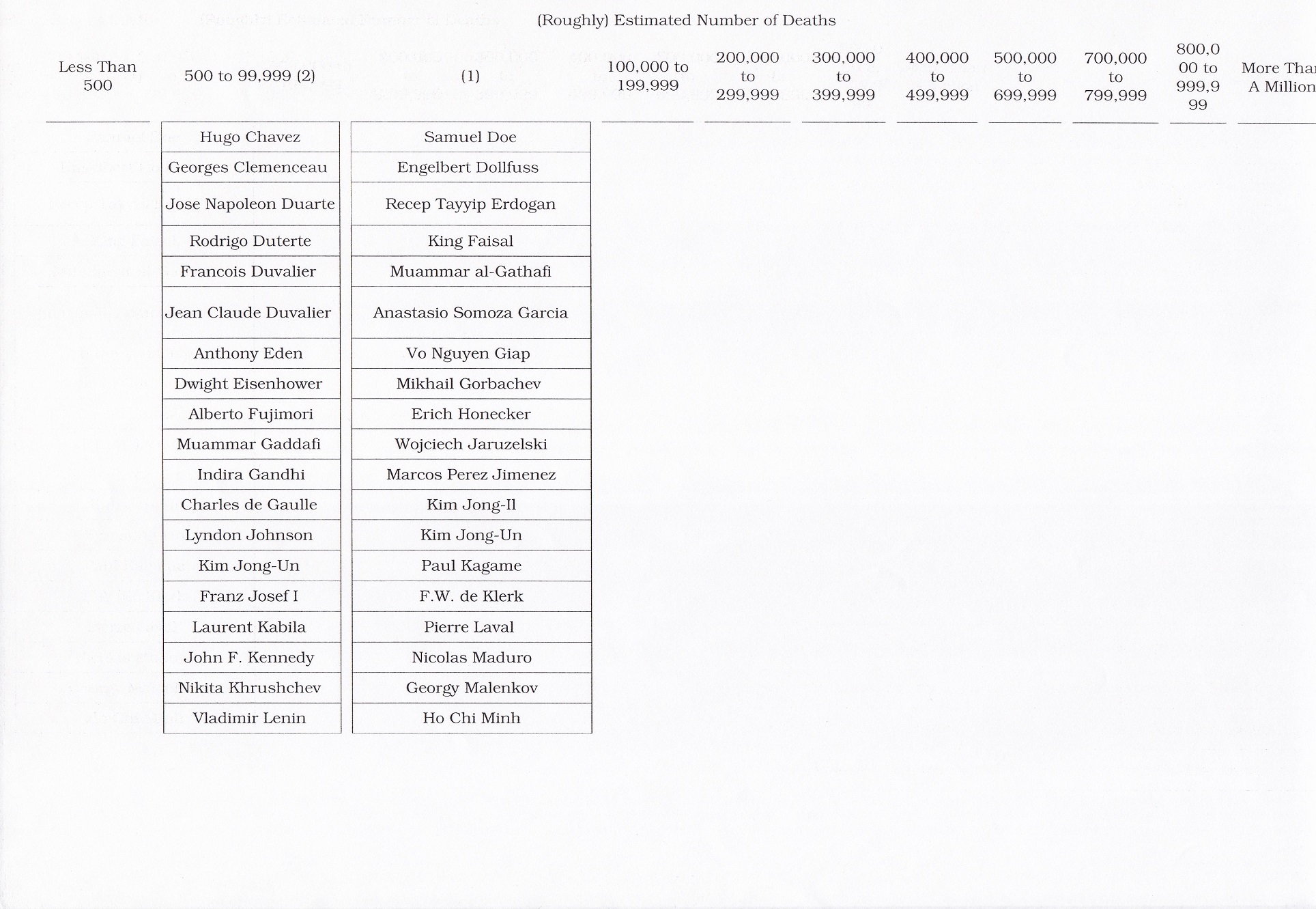
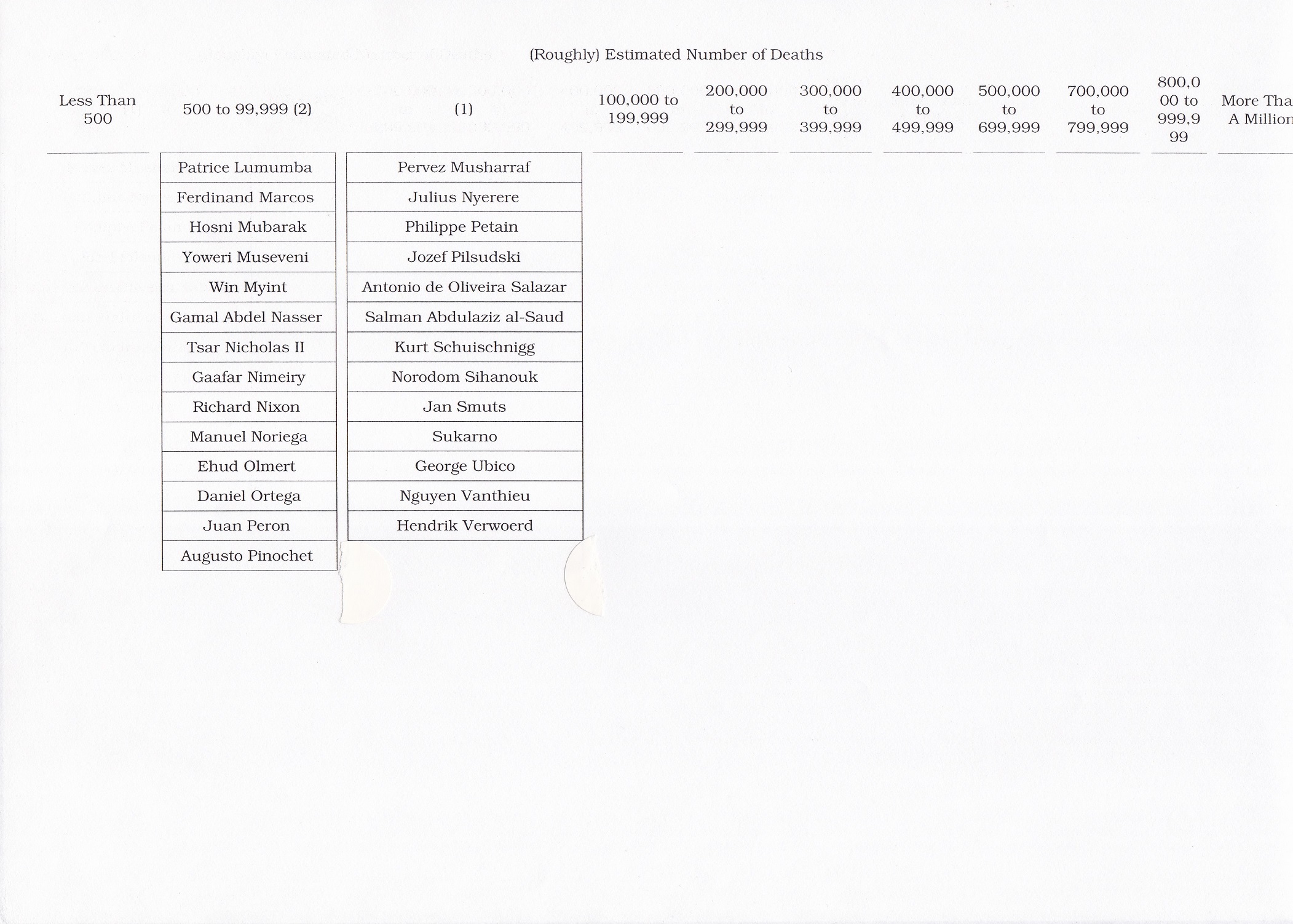
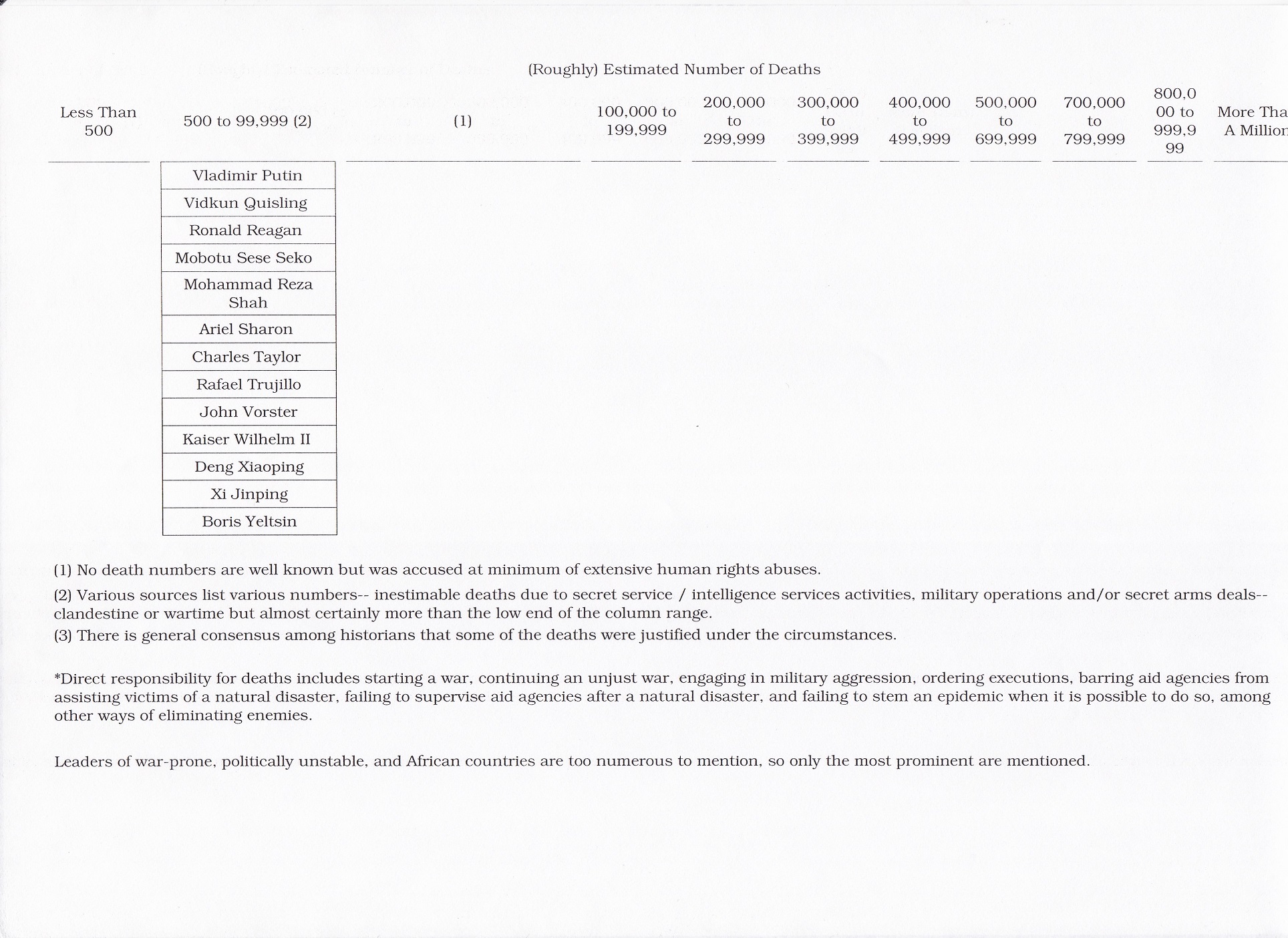
The Books of the Week are “Herbert Hoover, A Life” by Glen Jeansonne with David Luhrssen, published in 2016 and “Hubert Humphrey, A Biography” by Carl Solberg, published in 1984. Both of these slightly sloppily edited, structurally flawed– redundant– volumes described charismatic, liberal twentieth-century politicians. The Republican and Democratic leaders respectively were blamed for major adverse historical events over which they had largely no control.
The Humphrey book’s last chapter summarized all of its previous contents. This chapter would be a good reading assignment for a college class, as it provided a substantive overview of the man’s political career.
Sadly, Herbert Hoover and the Great Depression are inseparable whenever either is mentioned, due to vicious scapegoating. Yet, “Hoover fed an estimated 83 million people and was doubtless responsible for saving more lives than any individual in history.” Additionally, “Hoover took responsibility for errors and shunned credit helping to develop ties of trust in both directions.”
Born in 1874 in Iowa, Hoover grew up in a Quaker family in an agricultural community. He enjoyed outdoor farm chores better than school. His father died of typhus when he was six; his mother, of pneumonia when he was nine. In his teens, he moved to the Oregon home of his uncle, a medical doctor.
Hoover was in the first graduating class of Stanford University. Eventually, he successively managed large mining operations in various nations, that provided raw materials for weaponry. Thus, his vast wealth continued to snowball at an even faster pace with the start of WWI.
Ironically, Hoover was a humanitarian. In the nineteen-teens, he got permission from warring nations to deliver food to Germany-occupied Belgium to ward off famine there; northern France, too. Germany conceded because it feared that if Belgium starved, the United States might enter the war. Further, Hoover made sure that he, as the leader of the privately funded group that transported the food, refrained from engaging in war profiteering. The group boasted only one percent fixed costs, and when it was dissolved, donated its $35 million surplus to colleges in Belgium, as well as to a Belgian-American exchange program. To top it off, Hoover collected no salary.
Hoover was able to make Americans feel proud that they helped the Allies win the war by not wasting food in their own country. They internalized Hoover’s message via radio, newsreels, feature films and celebrity appearances from May 1917 through April 1919. Then in 1921, he began a food program for the Soviets. According to the author, “After the Great Engineer morphed into perhaps the greatest secretary of commerce in history, he was noted for his kind treatment of everyone who worked for him, as was the case when he became president.”
Hoover was a conservative capitalist– advocating a low income tax to aid business activities but high estate taxes to prevent perpetuities. Tax cuts, plus new technologies in the utilities, entertainment and automotive industries fueled tremendous economic growth between 1922 and 1928. Hoover convinced president Calvin Coolidge to let him meddle in all government affairs, in addition to his own domain– domestic and international commerce.
When Coolidge declined to run for reelection in the summer of 1927, Hoover let his friends speak for him in public about how great a president he himself would be. Those friends included all manner of journalists, authors, college communities, senators, business leaders, etc. Upon his election, he collected no government pay and he paid all his own expenses, including those covering White House entertainment.
Hoover filed more antitrust lawsuits than under any president before him. However, “By 1929, some of the nation’s most eminent businessmen– including Joseph P. Kennedy, Bernard Baruch, and Herbert Hoover– began to quietly divest themselves of stocks.”
In 1928, the world was heading for economic disaster for several reasons. American bankers lent money to European governments at usurious interest rates because they could, and Central and Eastern European governments sold bonds at interest rates they couldn’t possibly afford to make good on, because they needed to– debt from WWI was sky-high for a lot of countries.
The war had produced widespread destruction and serious shortages of resources of all kinds. American citizens were going crazy engaging in short-term trading rather than long-term investing in the stock market. There were massive political upheavals in Russia, Asia, Europe and Latin America. A government cannot create wealth, it can only redistribute it.
When the Depression hit, Hoover attempted to help Americans, even at political cost to himself. He argued that local and state governments rather than the federal government, should provide financial aid to their people because they knew their local residents’ needs better than the latter.
Read the book to learn the outcomes of Hoover’s arms-control summits; how he dealt with WWI veterans who demanded that their bonuses be paid early; why he was against the New Deal; the idealistic goal of Stanford’s Institution on War, Revolution, and Peace, which he founded; and much more.
Born in May 1911 in a small town in Minnesota, Hubert Humphrey graduated first of sixteen students from his high school class. Due to his family’s dire financial situation, he was forced to become a druggist in his family’s store for several years. He then was able to get married and attend the University of Minnesota. In order to afford school, he did all different low-level odd jobs while he took one and a half times the course load of normal students. He wanted to go to graduate school but his first child put the kibosh on that.
Skilled at debating and delivering speeches, Humphrey was pressured by friends and colleagues into becoming a politician rather than a teacher. In 1945, he was elected mayor of Minneapolis. Part of his platform from the get-go, and throughout his career was civil rights. Workaholic that he was, when running for the U.S. Senate in 1948, he traveled to all 87 of Minnesota’s counties at least twice– 31,000 miles, making seven hundred speeches. He hardly ever saw his growing family.
Humphrey was pro-union but he was no Communist. At the same time, in 1951 he agreed with Senator William Benton of Minnesota that Joseph McCarthy was using “Hitler’s Big Lie techniques.” In summer 1953, he took a page from Herbert Hoover’s playbook by creating an organization that used surplus crop yields from Minnesota to feed the hungry peoples of foreign nations.
Unfortunately, beginning in early 1966, when he was vice president, Humphrey became President Lyndon Johnson’s slavish mouthpiece on Vietnam. He visited the war zone and got it in his head that China was provoking aggression against the U.S. He had developed the same hubris syndrome as the president.
In late winter 1968, the controlling Johnson (finally, inconsiderately) withdrew from the presidential campaign. It was Humphrey’s turn to run for the head job. He was able to raise funds from wealthy sources who hated Robert Kennedy. But his campaigns had and always would have shoestring budgets. And after Kennedy was shot, Humphrey donors switched their allegiance to Republicans.
The two remaining Democratic candidates, Humphrey and Gene McCarthy, had survivor’s guilt. Psychologically, Johnson was like a father figure to the former, and he couldn’t, and didn’t become his own man until many years later.
One campaign promise Humphrey finally made in late September 1968, was to stop the bombing of Vietnam if the demilitarized zone was restored. The book’s author wrote that the “China Lobby” was again interfering with an American presidential election, as it had in 1948. In the earlier year, the China Lobby consisted of a “shadowy coterie of exiles and lobbyists” who sought to elect a Republican rather than reelect the Democrat Harry Truman because a Republican would be more likely to reverse U.S. policy and help Generalissimo Chiang Kai-Shek become the clear-cut, recognized leader of China. Well, it didn’t work. But, according to the author, the China Lobby’s activities worked in 1968.
A high-level Nixon campaign staff member named Madame Anna Chan Chennault pulled strings with the president of South Vietnam, Nguyen Van Thieu, convincing him to concoct some last-minute objections to peace negotiations– adding conditions for stopping the bombing– as an excuse for boycotting talks in Paris. Thieu was teasing Humphrey and made him lose to Nixon because Humphrey couldn’t tell American voters that he could stop the bombing. Thieu thought Nixon would give him more of what he wanted. In late October, Johnson– still president at the time– tacitly conspired with Nixon. Johnson wouldn’t allow Humphrey to attend the meeting with Nixon and George Wallace where they talked to Thieu via conference call.
However, a week before election day, Johnson– no skin off his nose– did attend Humphrey’s rally at the Houston Astrodome to say nice things about him. The candidate thought that three things were required for him to get elected: a robust economy, a possibility that the (evil) Nixon could win (which voters would chafe at), and peace in Vietnam. The third thing was obviously lacking.
Humphrey was made aware of the China Lobby situation before election day. But he naively thought that Nixon didn’t know of Madame Chennault’s influence on President Thieu. His magnanimous nature led him to omit mention of the conspiracy against himself in his speeches to voters.
Early on election day, California governor Jesse Unruh lied to voters, telling them that Humphrey would win California. So lots of voters who believed him didn’t bother to vote– they thought Humphrey had won already.
Read the book to learn of many more anecdotes regarding Humphrey’s too-nice nature, and much more about his whole life.